An Apple patent (number 20100202630) has appeared at the US Patent & Trademark Office for a method and system for approximating graphic equalizers using dynamic filter order reduction. It relates to media devices and, more particularly, to equalizer effects for media being presented on media devices.
Improved approaches to flexibly implementing graphic equalizers on media players are disclosed. These approaches provide dynamic order reduction of a multi-band graphic equalizer so that equalizer effects can be timely performed with only limited computational resources. In one embodiment, a media player receives a media item and associated equalizer settings for a multi-band graphic equalizer.
The media player can then automatically (i.e., without user action) approximate the multi-band graphic equalizer with the equalizer settings for the media item using a fewer number of filters. Fewer filters means order reduction, and thus reduction in computational requirements. After the multi-band graphic equalizer is approximated, the media player can present the media item to its user in accordance with the reduced complexity, approximated equalizer. The inventors are Aram Lindahl and Joseph Mark Williams.
Here’s Apple’s summary of the invention: “Media players, such as digital media players, are specialized portable computing devices that store and present (e.g., play, display) digital media (e.g., music, videos, or images). Often media players are small hand-held devices with limited media storage capacity and limited media management capability. As a result, media players typically associate with a host computer. The host computer can utilize an application resident on the host computer to perform media management for the host computer and the media player, such management including transfer of the media items and their attributes between the host computer and the media player. One such application is iTunes, produced by and available from Apple Inc. of Cupertino, Calif. An example of a popular media player is an iPod. which is also produced by and available from Apple Inc.
“iTunes can display a graphic equalizer for a user of the host computer. With iTunes, users can specify a set of equalizer settings by selecting one of a list of equalizer presets. Equalizer presets are equalizer settings for various frequency bands that are predetermined and available for selection by users. In addition, users can manually change the settings of a graphic equalizer to achieve a desired (e.g., custom) frequency response for particular media items. To a limited extent, equalizer settings for media items can be transferred from iTunes to the media player.
“Media players typically have limited computational resources and a small form factor. Consequently, there are difficulties with implementing a graphic equalizer on a media player. One prior solution involves manual conversion of predetermined equalizer settings for the equalizer presets to a simplified filter structure. Such a manual conversion can reduce computational requirements needed to implement the equalizer adjustments on the media player.
“Unfortunately, however, this prior solution based on manual conversion is time consuming and only effective when the equalizer settings are known and remain fixed. Since the equalizer settings must be fixed, the prior solution also does not support user manipulation of equalizer settings. Other prior solutions involve complex optimization algorithms and/or curve fitting of finite impulse response (FIR) filters. However, these approaches are computationally intensive and not guaranteed to find acceptable solutions, and the resulting filter is usually two or more orders of magnitude more computationally expensive than the original graphic equalizer. Thus, there is a need for improved approaches to flexibly implement graphic equalizers on media players with limited computational resources.
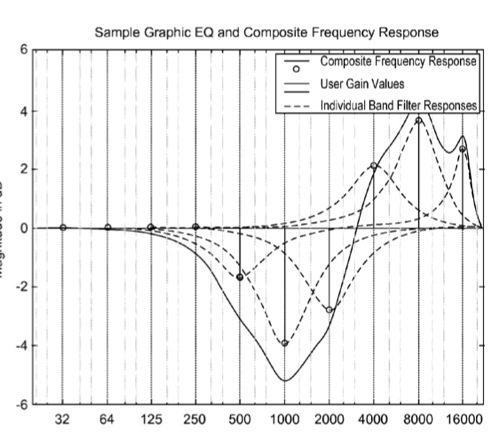
“Broadly speaking, the invention relates to improved approaches to flexibly implement graphic equalizers on media players. Media players are computing devices that are capable of storing and presenting (e.g., play, display) digital media (e.g., music, videos, or images). Media players typically have limited computational resources and are often portable or small in scale (e.g., hand-held). According to one aspect of the invention, dynamic order reduction of a multi-band graphic equalizer can be timely performed using only limited computational resources.
“In one embodiment, a media player receives a media item and associated equalizer settings for a multi-band graphic equalizer. In one implementation, equalizer settings (which are one type of quality setting) can be established for the media items on a media item by media item basis. The media player can then automatically (i.e., without user action) approximate the multi-band graphic equalizer with the equalizer settings for the media item using a fewer number of filters. Fewer filters means order reduction, and thus reduction in computational requirements. After the multi-band graphic equalizer is approximated, the media player can present the media item to its user in accordance with the reduced complexity, approximated equalizer.
“Graphic equalizers are used to shape audio frequency responses to a user’s preference. The equalizer settings of a multi-band graphic equalizer can be provided to the media player from a host computer. In such case, each media item can have their own equalizer settings. Alternatively, each user can have their own equalizer settings. As an example, the host computer can transfer not only media items but also associated equalizer settings to a media player during a synchronization operation. In another embodiment, equalizer settings can be manipulated locally by a user of the media player. Local manipulation of equalizer settings can provide real-time equalizer adjustment at the media player.
“The invention can be implemented in numerous ways, including as a method, system, device, apparatus, or computer readable medium.”