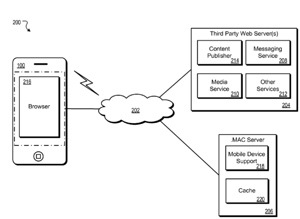
Apple has won a patent (number 7921187) for a newsreader for a mobile device.
Per the patent, providing information to a mobile device can include receiving a translation request from a mobile device, wherein the translation request includes a resource locator identifying information in a native format; accessing the information identified by the resource locator, wherein the information is retrieved from a local cache if available and otherwise is retrieved from a source associated with the resource locator; translating at least a portion of the information identified by the resource locator to generate a translated file in a supported format; and transmitting the translated file to the mobile device.
Further, the information retrieved from a source associated with the resource locator can be stored in the local cache. Additionally, the information identified by the resource locator can be cleared from the local cache after a predetermined amount of time. The inventors are Stephane Lunati, Ken Goto, John Martin, May-Li Khoe and Helan Ma.
Here’s Apple’s background and summary of the invention: “Mobile devices can be configured to access and retrieve content, including web pages and multimedia content, over a wireless network connection. A wide variety of wireless protocols have been established to support wireless communications via a mobile device. For example, a mobile device can establish a wireless network connection through an access point, such as a cellular network or a wireless access point, including an 802.11g access point and a Wi-Fi hot spot.
“Once connected, the mobile device can access a number of information sources, including the internet and private networks. Further, the mobile device can use the wireless connection to receive e-mail messages, retrieve electronic documents, and access content servers to browse web pages. The types of information that can be presented on a mobile device have been expanded in recent years to include high-resolution images and multimedia streams.
“Further, a mobile device can access one or more data feeds over the wireless data network. A data feed can be characterized by a particular web feed format, such as an RSS (Really Simple Syndication, RDF Site Summary, or Rich Site Summary) feed. RSS describes a family of web feed formats used to publish frequently updated content, including blog entries, news stories and headlines, podcasts, and job listings. An RSS document, which is referred to as a feed, a web feed, or a channel, can contain either a summary of content from an associated web site or a full text version of the web content. For example, an RSS feed can be employed for web syndication, in which one or more portions of content from a source web site are made available for use on other web sites. Further, the RSS feed can be used to identify the information most recently made available on a source web site, such as the latest news stories, forum posts, and listings.
“A mobile device executing a function limited application, such as a browser or reader application, can be configured to transmit a request for one or more items of content to an information provider. Further, the mobile device can be configured to determine whether information received in response to the request for content is supported by the function limited application hosted on the mobile device.
“For example, the mobile device can examine a content-type header received from an information provider to determine whether any unsupported content is being received, such as an RSS feed. In order to permit mobile access to a variety of information sources and content types, the present inventors recognized the need to request from a service provider reformatted or translated content corresponding to one or more types of unsupported content.
The present inventors also recognized the need for a service provider to cache original source content for which translated content has been previously requested. Further, the need to cache translated content corresponding to the original source content also was recognized. Additionally, the present inventors also recognized the need to structure the translated content in a single file to permit users to quickly navigate through the translated content. Accordingly, the techniques and apparatus described here implement algorithms for requesting, translating, and caching content for use on a mobile device.
“In general, in one aspect, the subject matter can be implemented to include receiving a translation request from a mobile device, wherein the translation request includes a resource locator identifying information in a native format; accessing the information identified by the resource locator, wherein the information is retrieved from a local cache if available and otherwise is retrieved from a source associated with the resource locator; translating at least a portion of the information identified by the resource locator to generate a translated file in a supported format; and transmitting the translated file to the mobile device.
“The subject matter also can be implemented such that the native format corresponds to an RSS feed. Further, the subject matter can be implemented to include storing in the local cache the information retrieved from a source associated with the resource locator. clearing the information identified by the resource locator from the local cache after a predetermined amount of time.
“The subject matter also can be implemented to include storing the translated file in the local cache, wherein the translated file is associated with the information identified by the resource locator. The subject matter further can be implemented to include determining that the information identified by the resource locator has been updated at the source associated with the resource locator; and clearing the translated file from the local cache. Additionally, the subject matter can be implemented to include automatically generating the translation request, by the mobile device, in response to receiving information associated with the resource locator in an unsupported format.
“The subject matter also can be implemented such that the mobile device detects the unsupported format based on a value included in a content-type field. The subject matter further can be implemented such that the translated file comprises a HyperText Markup Language file. Additionally, the subject matter can be implemented to include displaying the translated file as an index including a plurality of links, wherein selecting a link causes a first portion of the translated file to be hidden and a second portion of the translated file to be displayed.
“In general, in another aspect, the subject matter can be implemented as a computer program product, encoded on a computer-readable medium, operable to cause data processing apparatus to perform operations comprising receiving a translation request from a mobile device, wherein the translation request includes a resource locator identifying information in a native format; accessing the information identified by the resource locator, wherein the information is retrieved from a local cache if available and otherwise is retrieved from a source associated with the resource locator; translating at least a portion of the information identified by the resource locator to generate a translated file in a supported format; and transmitting the translated file to the mobile device.
“Further, the subject matter can be implemented such that the native format corresponds to an RSS feed. The subject matter also can be implemented to be further operable to cause data processing apparatus to perform operations comprising storing in the local cache the information retrieved from a source associated with the resource locator. Additionally, the subject matter can be implemented to be further operable to cause data processing apparatus to perform operations comprising clearing the information identified by the resource locator from the local cache after a predetermined amount of time.
“The subject matter also can be implemented to be further operable to cause data processing apparatus to perform operations comprising storing the translated file in the local cache, wherein the translated file is associated with the information identified by the resource locator. Further, the subject matter can be implemented to be further operable to cause data processing apparatus to perform operations comprising determining that the information identified by the resource locator has been updated at the source associated with the resource locator; and clearing the translated file from the local cache. Additionally, the subject matter can be implemented to be further operable to cause data processing apparatus to perform operations comprising automatically generating the translation request, by the mobile device, in response to receiving information associated with the resource locator in an unsupported format.
“Further, the subject matter can be implemented such that the mobile device detects the unsupported format based on a value included in a content-type field. The subject matter also can be implemented such that the translated file comprises a HyperText Markup Language file. Additionally, the subject matter can be implemented to be further operable to cause data processing apparatus to perform operations comprising displaying the translated file as an index including a plurality of links, wherein selecting a link causes a first portion of the translated file to be hidden and a second portion of the translated file to be displayed.
“The techniques described in this specification can be implemented to realize one or more of the following advantages. For example, the techniques can be implemented such that one or more types of content that are not supported by a function limited application can be translated into a supported format. The techniques also can be implemented such that the request for translated information can be automatically generated upon detecting that content is being received in an unsupported format.
“The techniques further can be implemented to include caching at a service provider one or more of the source content represented in an unsupported format and the translated content corresponding to the source content. Additionally, the techniques can be implemented to include automatically transmitting a request for translated content in response to detecting the receipt of information in an unsupported format.”
— Dennis Sellers