A new Apple patent (number 20120011227) for techniques and systems for supporting podcasting has appeared at the U.S. Patent & Trademark Office.
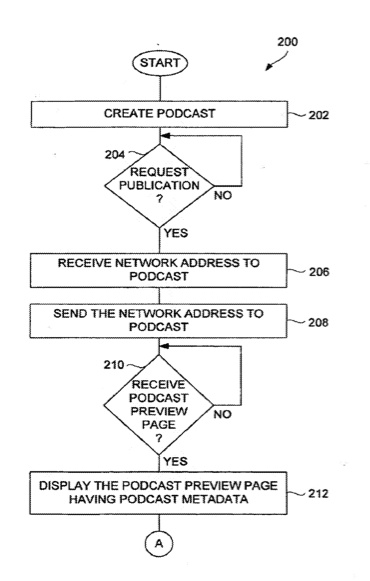
Improved podcasts and techniques that facilitate their use are disclosed. The improved techniques can pertain to creating, publishing, hosting, accessing, subscribing, managing, transferring, and/or playing podcasts. According to one aspect, a client application can subscribe to podcasts and then automatically monitor the podcasts for updates to be downloaded. In the event that user interest in a podcast becomes inadequate, downloading of further updates can be restricted.
According to another aspect, a podcast can be subscribed to through use of a portable subscription file. According to still another aspect, podcast feeds can be enhanced to include segment elements and other metadata. The inventors are Anne Jones, Thomas Dowdy, Jeffrey Robbin, Mike Wiese and Stephen Davis.
Here’s Apple’s background and summary on the invention: “A media player stores media assets, such as audio tracks, that can be played or displayed on the media player. One example of a portable media player is the iPod.RTM. media player, which is available from Apple Computer, Inc. of Cupertino, Calif. Often, a media player acquires its media assets from a host computer that serves to enable a user to manage media assets.
“In managing media assets, a user can create playlists for audio tracks. These playlists can be created at the host computer. Media assets within the playlists can then be copied to the media player. As an example, the host computer can execute a media management application to create and manage media assets. One example of a media management application is iTunes.RTM. produced by Apple Computer, Inc.
“Podcasts are typically used to share content from websites. Podcasts are associated with Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feeds which use a lightweight XML format. A podcast can be organized into episodes much like a radio or television program. An interested person can subscribe to receive podcast episodes that are subsequently published. This is achieved by the interested person using their computer to access a podcast website that hosts the RSS feed. The interested person can then subscribe the RSS feed such that their computer occasionally re-visits the podcast website to check for any new podcast episodes.
“Typically, if a new podcast episode is available, it is downloaded to the computer. Thereafter, the interested user can play the podcast episode at their computer in the same manner as other audio files (e.g., MP3 files). A utility program can be used to download the audio files to a portable media player (e.g., MP3 player). One example of such a conventional utility program is “iPodder” which is a small program that runs on one’s computer to download audio files to one’s portable media player.
“Unfortunately, podcasts are conventionally not easily managed on host computer. Podcasts often dynamically change as new episodes are released. Management of such dynamic media assets is complicated. Additionally, to the extent that the host computer desires to support a portable media player, the host computer needs to manage the transfer of podcast data to the portable media player. Thus, there is a need for techniques to manage and use podcasts on computers.
“The invention pertains to improved podcasts and techniques that facilitate their use. The improved techniques can pertain to creating, publishing, hosting, accessing, subscribing, managing, transferring, and/or playing podcasts.
“According to one aspect, a client application can subscribe to podcasts and then automatically monitor the podcasts for updates. When updates to the podcasts are available (e.g., new episodes), the updates can be downloaded to the client application. However, in the event that user interest in a podcast becomes inadequate, downloading of further updates can be restricted. According to another aspect, a podcast can be subscribed to through use of a portable subscription file.
“The portable subscription files are portable and transferable across networks, thereby providing a convenient way to facilitate subscription to podcasts. According to still another aspect, podcast feeds can be enhanced to include segment elements and other metadata. The segment links and time indications can be provided for each of the segments. A client application that present a podcast to a user can provide an improved graphical user interface through use of the segment elements and other metadata.
“The invention can be implemented in numerous ways, including as a method, system, device, apparatus (including graphical user interface), or computer readable medium. Several embodiments of the invention are discussed below.
“As a method for subscribing to a podcast, one embodiment of the invention includes at least the acts of: receiving a portable subscription file that is used to facilitate subscribing to the podcast; accessing the portable subscription file to obtain podcast information; and subscribing to the podcast using the podcast information.
“As a computer readable medium including at least computer program code for subscribing to a podcast, one embodiment of the invention includes at least: computer program code for receiving a user selection of a portable subscription file that is used to facilitate subscribing to the podcast; computer program code for launching a media management application in response to the user selection; computer program code for parsing the portable subscription file to obtain podcast information; and computer program code for subscribing to the podcast via the media management application using the podcast information.
“As a portable subscription file, one embodiment of the includes at least: an application identifier; and a network address for a podcast feed.
“As a method for acquiring podcast information at a client application, the podcast information being acquired from a podcast hosting server via a network, one embodiment of the invention includes at least the acts of: accessing a podcast feed from the podcast hosting server via the network to acquire episode information for the podcast; determining one or more new episodes based on the acquired episode information; determining whether the podcast is still active at the client application; and receiving, at the client application, the one or more new episodes from the podcast hosting server over the network so long as it is determined that the podcast is still active at the client application.
“As a computer readable medium including at least computer program code for acquiring digital multimedia asset information at a client application, the digital multimedia asset information being acquired from a digital multimedia asset hosting server via a network, one embodiment of the invention includes at least: computer program code for accessing a digital multimedia asset feed from the digital multimedia asset hosting server via the network to acquire episode information for the digital multimedia asset; computer program code for determining one or more new episodes based on the acquired episode information; computer program code for determining whether the client application or a user thereof has shown adequate interest in the digital multimedia asset; and computer program code for receiving, at the client application, the one or more new episodes from the digital multimedia asset hosting server over the network so long as it is determined that the client application or a user thereof has shown adequate interest in the digital multimedia asset.
“As a podcast feed, one embodiment of the invention includes a plurality of segment elements, each of the segment elements including a segment link for a multimedia element and a time indication associated with the segment elements.”